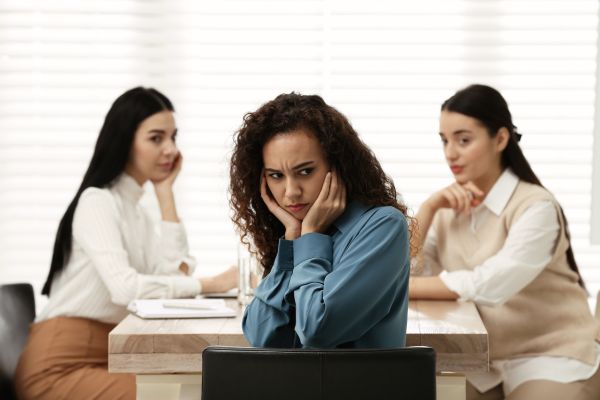
Workplace harassment is an issue that continues to affect countless professionals worldwide. It undermines not only the dignity of employees but also the integrity of organizations. Understanding what constitutes workplace harassment, how to recognize it, and knowing your legal rights are essential steps in fostering a safe and productive work environment.
Understanding Workplace Harassment
Workplace harassment refers to unwelcome behavior that creates an intimidating, hostile, or offensive work environment. This can include verbal remarks, physical actions, or even subtle gestures that target a person’s race, gender, religion, age, disability, or other protected characteristics. It is not limited to overt acts; even seemingly minor incidents can accumulate into a pervasive problem that affects an individual’s mental health and professional performance.
The term covers a broad spectrum of misconduct. Sexual harassment, a common subtype, involves inappropriate comments, advances, or requests for favors in exchange for career benefits. Similarly, discriminatory harassment targets individuals based on characteristics protected under employment laws. Bullying, intimidation, and retaliation also fall under the umbrella of workplace harassment.
Recognizing the Signs of Harassment
Recognizing workplace harassment is not always straightforward. Often, victims may dismiss early signs or fear retaliation if they speak out. Persistent jokes or comments about appearance, repeated exclusion from meetings, undermining professional contributions, and spreading rumors are all red flags. Employees should remain vigilant to subtle forms of harassment, such as microaggressions, which can have long-term emotional consequences.
Witnesses also play a crucial role. Colleagues who observe inappropriate conduct have a responsibility to support affected coworkers and, where possible, report the behavior to management or human resources. Silence enables toxic workplace cultures to flourish, while proactive action can help break the cycle.
The Legal Framework Surrounding Workplace Harassment
Most countries have established legal protections to address workplace harassment. In the United States, Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 prohibits harassment based on race, color, religion, sex, or national origin. The Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) enforces these laws and provides a clear path for filing complaints.
In other regions, similar legislation exists. The UK’s Equality Act 2010 offers protection against harassment related to protected characteristics, while countries like Canada and Australia have federal and provincial laws in place to safeguard employees. These laws typically require employers to provide a harassment-free workplace and establish procedures for addressing complaints.
It is vital for employees to familiarize themselves with their local legal framework. Knowing your rights empowers you to take informed action if harassment occurs.
Employer Responsibilities and Preventative Measures
Employers bear a significant responsibility in preventing and addressing workplace harassment. They are legally obligated to create a safe work environment by implementing anti-harassment policies, offering regular training, and providing accessible reporting mechanisms.
An effective anti-harassment policy should clearly define unacceptable behavior, outline reporting procedures, and describe the consequences for perpetrators. Regular training helps employees understand their rights and responsibilities while fostering a culture of respect and inclusion.
When a complaint is filed, employers must investigate promptly and impartially. Retaliation against individuals who report harassment is unlawful, and organizations must ensure protection for those who come forward.
Taking Action Against Workplace Harassment
If you experience workplace harassment, document each incident meticulously, noting dates, times, locations, and details of what occurred. This record can provide crucial evidence should you decide to file a complaint internally or with a regulatory body.
Begin by reporting the issue through your company’s internal channels, such as human resources or designated ethics officers. If the matter remains unresolved or the company fails to act, legal recourse may be necessary. Consulting with an employment lawyer can provide clarity on your options and guide you through the process.
Remember, the law protects employees from retaliation, and taking action is a vital step towards safeguarding not only your own rights but also the rights of others in your workplace.
Building a Culture Free from Harassment
Addressing workplace harassment requires collective effort. Organizations must foster environments where respect, diversity, and inclusion are prioritized. Leadership plays a key role in modeling appropriate behavior and ensuring accountability at all levels.
Employees should feel empowered to speak up, knowing their concerns will be taken seriously and handled appropriately. Open communication, clear policies, and ongoing education are essential elements in building a workplace culture where harassment is not tolerated.
Conclusion
Workplace harassment is a serious issue that demands attention from both employers and employees. By understanding what constitutes harassment, recognizing the signs, and knowing your legal rights, you can help create a safer and more respectful work environment. Organizations that prioritize anti-harassment measures not only protect their workforce but also enhance productivity and morale. Remember, taking a stand against workplace harassment is not just a legal right – it is a moral responsibility to ensure every professional can work without fear or intimidation.